
Pupils extend their use of the properties of shapes.

Non-statutory guidance: Pupils’ knowledge of the properties of shapes is extended at this stage to symmetrical and non-symmetrical polygons and polyhedra.Draw 2-D shapes and make 3-D shapes using modelling materials and recognise 3-D shapes in different orientations and describe them.Pupils identify, compare and sort shapes on the basis of their properties and use vocabulary precisely, such as sides, edges, vertices and faces.
Non-statutory guidance: Pupils handle and name a wide variety of common 2-D and 3-D shapes, including quadrilaterals and polygons, and cuboids, prisms and cones, and identify the properties of each shape (for example, number of sides, number of faces).Compare and sort common 2-D and 3-D shapes and everyday objects.Identify 2-D shapes on the surface of 3-D shapes,.
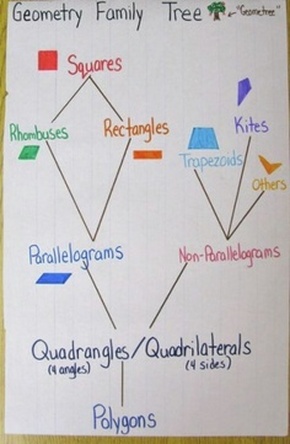
 Identify and describe the properties of 3-D shapes, including the number of edges, vertices and faces. Identify and describe the properties of 2-D shapes, including the number of sides and line symmetry in a vertical line. They recognise these shapes in different orientations and sizes, and know that rectangles, triangles, cuboids and pyramids are not always similar to each other. Non-statutory guidance: Pupils handle common 2-D and 3-D shapes, naming these and related everyday objects fluently. Recognise and name common 2-D and 3-D shapes, including: 2-D shapes 3-D shapes. Here’s what the National Curriculum expects to be taught about 2D shapes: 2D shapes in Year 1 Geometry is taught in every year group in KS1 and KS2. Read more: 2D And 3D Shapes: Properties of Shapes When do children learn about 2D shapes in primary school? A heptagon or septagon is any shape with 7 sides. A parallelogram has two pairs of parallel lines and opposite equal angles. A trapezium has one pair of parallel lines. A rhombus has two pairs of parallel lines, as well as equal sides and opposite equal angles. A rectangle has two pairs of parallel straight lines and each angle equals 90°. A kite has two pairs of equal-length sides and the diagonals cross at right-angles. A square is a regular quadrilateral and each angle equals 90°. An isosceles triangle has two sides and two angles that are the same.
Identify and describe the properties of 3-D shapes, including the number of edges, vertices and faces. Identify and describe the properties of 2-D shapes, including the number of sides and line symmetry in a vertical line. They recognise these shapes in different orientations and sizes, and know that rectangles, triangles, cuboids and pyramids are not always similar to each other. Non-statutory guidance: Pupils handle common 2-D and 3-D shapes, naming these and related everyday objects fluently. Recognise and name common 2-D and 3-D shapes, including: 2-D shapes 3-D shapes. Here’s what the National Curriculum expects to be taught about 2D shapes: 2D shapes in Year 1 Geometry is taught in every year group in KS1 and KS2. Read more: 2D And 3D Shapes: Properties of Shapes When do children learn about 2D shapes in primary school? A heptagon or septagon is any shape with 7 sides. A parallelogram has two pairs of parallel lines and opposite equal angles. A trapezium has one pair of parallel lines. A rhombus has two pairs of parallel lines, as well as equal sides and opposite equal angles. A rectangle has two pairs of parallel straight lines and each angle equals 90°. A kite has two pairs of equal-length sides and the diagonals cross at right-angles. A square is a regular quadrilateral and each angle equals 90°. An isosceles triangle has two sides and two angles that are the same.  A scalene triangle is an irregular triangle. A right-angled triangle is any triangle with one right angle. An equilateral triangle is a regular triangle and each angle equals 60°. A semi-circle has 2 sides 1 curved side and 1 straight side. Learning 2D shapes through Third Space Learning’s online interventions Properties of 2D shapesĪs well as the names, children need to know the properties of 2D shapes as listed below and in the printable table. When we move on to 3D shapes we talk about faces, edges and vertices. The properties of 2D shapes refer to their sides and angles. An irregular shape has different length sides and/or interior angles. A regular shape has all sides the same length and all interior angles the same size. A polygon is a 2D shape with straight sides. In primary school, children will learn about the following 2d shapes: polygons, regular and irregular shapes.
A scalene triangle is an irregular triangle. A right-angled triangle is any triangle with one right angle. An equilateral triangle is a regular triangle and each angle equals 60°. A semi-circle has 2 sides 1 curved side and 1 straight side. Learning 2D shapes through Third Space Learning’s online interventions Properties of 2D shapesĪs well as the names, children need to know the properties of 2D shapes as listed below and in the printable table. When we move on to 3D shapes we talk about faces, edges and vertices. The properties of 2D shapes refer to their sides and angles. An irregular shape has different length sides and/or interior angles. A regular shape has all sides the same length and all interior angles the same size. A polygon is a 2D shape with straight sides. In primary school, children will learn about the following 2d shapes: polygons, regular and irregular shapes. CLASSIFYING 2 DIMENSIONAL SHAPES DOWNLOAD
Download Free Now! Which 2D shapes do children learn about?








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
